In this detailed overview, we’ll look at the qualities, applications, and market trends of flat steel. You can also learn about the versatility of flat steel and its numerous applications in a variety of sectors. Learn about the industry trends and dynamics around flat steel, allowing you to make informed decisions and maximize its potential in your organization.
Flat steel is a type of steel product distinguished by its flat and rectangular shape. It is made by hot rolling, which involves heating the steel and passing it through a series of rollers to acquire the desired thickness and shape. The finished product has a consistent thickness, smooth surfaces, and straight edges.

Hot-rolled and cold-rolled flat steel are the most prevalent types of flat steel. Hot-rolled flat steel is made at high temperatures, which results in a scaled surface finish. It is frequently utilized in structurally demanding applications such as construction, infrastructure, and heavy machinery. In contrast, cold-rolled flat steel is treated at room temperature, resulting in a smoother and more exact surface finish. It is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, appliances, and electrical equipment.
Steel sheet/coil and steel plate are two typical names for flat steel products. Hot rolled coil (HRC), cold rolled coil (CRC), metallic coated steel, organic coated steel, coil plate, and reversing mill plate are some of the different varieties.
The majority of steel plate is produced in thicknesses ranging from 5 mm to 80mm. Plates are hot rolled coil overlaps in lower gauges. Steel plates are classified into two types: reversing mill plates and coil plates. Reversing mill plates are made by rolling a slab back and forth and have a higher thickness than coil plates. Coil plates, on the other hand, are produced by rolling in tandem mills in a single direction.
The thickness of steel sheet/coil is often less than 5mm. Hot-rolled sheet, cold-rolled sheet, metallic coated sheets, and organic coated sheets are also steel sheet products. Hot rolling is done when the recrystallisation temperature of steel exceeds 1700° F. Steel is easily deformed at this temperature. In comparison to cold rolled steel, HRC provides less precision and a lower surface polish after cooling.

HRC can be marketed for a variety of uses or further processed to produce cold rolled coils. Cold rolling is typically done at room temperature. It improves both the mechanical qualities and the surface finish.
CRC has a wide range of applications, primarily in construction and automotive. It can also be treated further to produce corrosion-resistant steel, often known as coated steel. Hot dip galvanized (HDG) steel is one of the most common varieties of metallic coated steel. It is zinc-coated to protect steel from corrosion by minimizing its exposure to the outside environment. Organic coated steel, also known as color coated steel or pre-painted galvanized iron (PPGI), can be made from metallic coated steel.
Flat steel comes in various forms, each tailored to specific applications. Here are some common types of flat steel:
Flat steel sheets are thin, flat pieces of steel with consistent thickness. They are commonly used in construction, automotive manufacturing, and general fabrication. Flat steel sheets can be cut, bent, and formed into various shapes and sizes.
Flat steel plates are thicker and sturdier than sheets. They are utilized in heavy-duty applications that require high strength and load-bearing capacity. Flat steel plates are commonly employed in construction projects, shipbuilding, and industrial machinery.

Flat steel bars have a rectangular cross-section and are available in various widths and thicknesses. They are used in construction, manufacturing, and engineering projects. Flat steel bars are commonly utilized as structural components, supports, and brackets.
Flat steel brackets are L-shaped components made from flat steel. They are widely used for supporting and joining structural elements in construction, furniture manufacturing, and shelving systems. Flat steel brackets provide stability and reinforcement.
Flat steel bars with holes are designed for easy fastening and installation. They feature pre-drilled holes along the length to accommodate bolts, screws, or other fasteners. These bars are commonly used in construction, infrastructure, and DIY projects.

Flat steel rods are long, slender pieces of steel with a flat cross-section. They are utilized in applications that require strength, rigidity, and stability. Flat steel rods are commonly employed in construction, fabrication, and machinery.
Each type of flat steel has unique characteristics and applications, allowing for versatility in various industries. The choice of flat steel type depends on factors such as desired strength, thickness, surface finish, and specific application requirements.
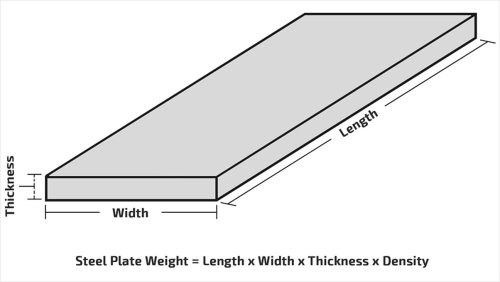
The weight and dimensions of flat steel plates are critical in a variety of industries and applications. Flat steel plates are available in a variety of sizes to satisfy the needs of certain projects. The weight of a flat steel plate is determined by its size, thickness, and steel density. Because of the higher amount of steel, thicker plates often weigh more than thinner ones.
Flat steel plates are available in a variety of standard sizes, ranging from tiny dimensions for basic production to larger dimensions for structural uses. Plate sizes vary depending on region and standard, although they often fall within a range of thicknesses and widths. Thicknesses can range from a few millimeters to several inches, and widths can range from a foot to several feet or more. Flat steel plate lengths are usually standardized to facilitate handling and transit.
Flat steel plate weight and size are critical issues in industries such as construction, manufacturing, shipbuilding, and infrastructure development. Engineers and designers choose the proper plate size and weight to meet structural integrity, load-bearing capacity, and overall project requirements. Understanding the weight and dimensions of flat steel plates enables for precise material planning, efficient fabrication processes, and maximum resource usage.
To gain exact information on the weight and sizes of flat steel plates for specific purposes, reference industry standards, specifications, and suppliers. Furthermore, technological developments in steel production have resulted in the availability of custom-cut plates, allowing for greater flexibility in addressing the needs of individual projects.

The weight and sizes of flat steel plates can vary significantly depending on the specific dimensions and thicknesses. However, here are some general examples to provide a sense of the weight and size ranges:
Common thicknesses for flat steel plates range from 1/8 inch (3.175 mm) to 1 inch (25.4 mm) or more.
Thicker plates, such as those used in heavy-duty applications, can have thicknesses exceeding 1 inch.
Flat steel plates typically come in widths ranging from 12 inches (304.8 mm) to 72 inches (1828.8 mm) or more.
Wider plates beyond 72 inches can also be available, depending on specific requirements.
The standard length of flat steel plates is commonly 96 inches (2438.4 mm) or 120 inches (3048 mm).
Longer lengths, such as 240 inches (6096 mm) or custom lengths, may be available based on project specifications.
The weight of a flat steel plate can be calculated by multiplying the plate’s length, width, and thickness with the density of the steel material.
The density of steel typically ranges from 7.85 g/cm³ to 8.05 g/cm³, depending on the specific grade.
It’s important to note that these numbers are general examples, and the actual weight and sizes of flat steel plates can vary depending on the specific standards, grades, and supplier specifications.
Flat steel prices are primarily determined by iron ore (raw material) pricing and slab (substrate for merchant/off-take agreement buyers). In Asia, there has been fierce competition from Russian and Indian HRC suppliers, as well as weak demand for finished steel in key slab importing countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, and Taiwan. This resulted in substantially cheaper slab prices when compared to Brazilian prices. Meanwhile, the downward trend has been stifled as slab suppliers declined to decrease their bids any more, claiming that they would be unable to recoup production expenses.
US purchasers have begun to return to the market in October, purchasing slabs from Brazil utilizing the remaining annual allotment (less than 0.5 Mt). This has aided Brazil’s export prices, which have reduced its loss from August levels to barely USD 5/t.

Flat steel is utilized in numerous applications. Steel plates are mostly utilized in ship construction. The shipbuilding sector is primarily concentrated in North East Asia, with Europe accounting for the second-largest share. Steel plate production and consumption are likewise in accordance with the shipbuilding sector, with North East Asia leading the way and Europe coming in second. Large-diameter steel pipes also employ steel plates. The majority of pipeline construction projects are taking place in North East Asia, North America, and Europe. Steel plates are used extensively in construction projects, particularly steel bridges, skyscrapers, and infrastructure.
Due to its cheaper cost compared to other further processed flat steel kinds, hot rolled coil is the most commonly utilized form of flat steel. It is commonly utilized in the construction industry for roofs, staircases, sheds, and welded structures. It is also utilized in machinery to make parts and structures, as well as as a substrate for small and medium diameter welded pipes. Packaging, railways, and automotive are among its other end users.
Cold rolled steel is mostly utilized in automobiles, including external and interior body elements. Because of its great formability and dent resistance, it is frequently employed in appliances. Its applications also include items that require a smooth surface finish. Engineering, white goods, precision welded tubes, appliances, furniture, cabinets, toolboxes, storage, light construction, and industrial applications are some of its end-use sectors.
Read more
Vietnam Ingots: Everything You Need to Know
What precisely is an iron ingot? The manufacturing of iron ingots
Overall, flat steel is a fundamental building material in numerous industries, playing a vital role in construction, manufacturing, transportation, and infrastructure development. Its properties, such as strength, formability, and versatility, make it a preferred choice for applications that demand structural integrity and reliability.
Address
Website: https://stavianmetal.com
Email: info@stavianmetal.com
