Aluminum extrusion is a versatile and flexible material widely used in everyday life. From construction to household appliance manufacturing, aluminum extrusion plays a crucial role in various fields. In this article, Stavian Industrial Metal will help you understand the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and how to choose a reputable supplier of aluminum extrusion products.
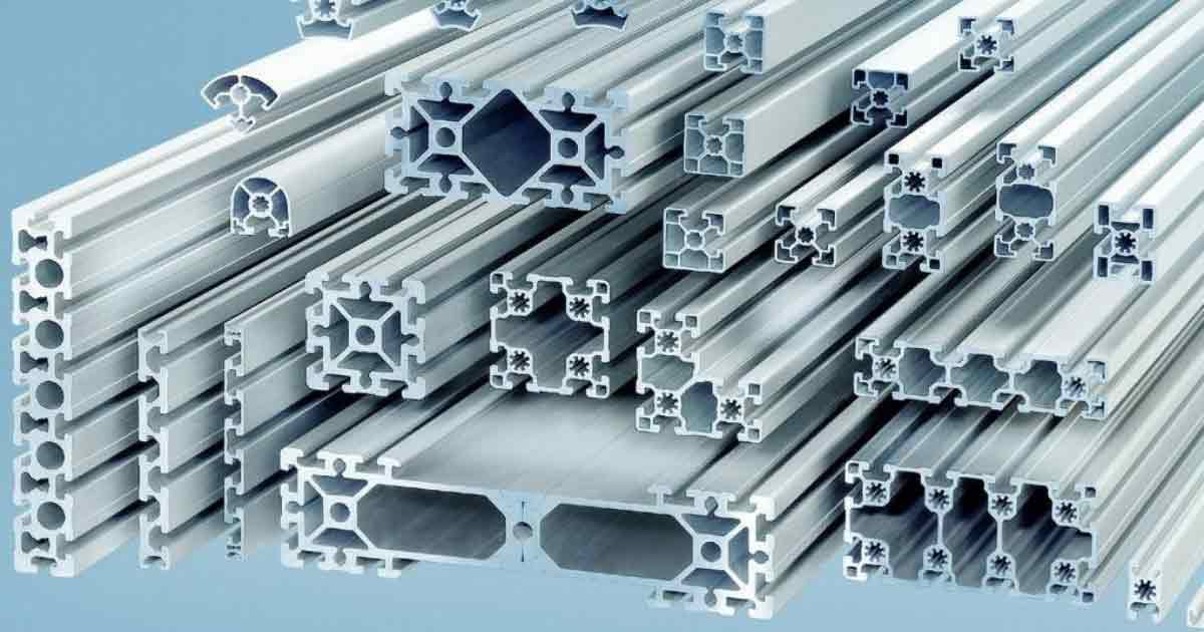

Understanding aluminum extrusion in the industrial metal field
Aluminum extrusion is a type of aluminum bar produced through a process where a billet is heated and then forced through a steel die under high pressure to create the desired shape. This process results in aluminum bars with high dimensional accuracy and uniform structure.
After being cut to the desired sizes, these aluminum bars undergo aging treatment to increase hardness and mechanical strength, making them suitable for various applications in different industries. This production method is ideal for large-scale manufacturing, requiring precision and uniformity in the final product.
Aluminum extrusion is produced by heating a billet and then forcing it through a steel die under high pressure to create the desired shape.
Aluminum extrusion is widely used in life due to the following outstanding advantages:
The process of heating aluminum billets to create aluminum extrusion forms predetermined cross-sections, providing convenience and numerous benefits for consumers in various applications.
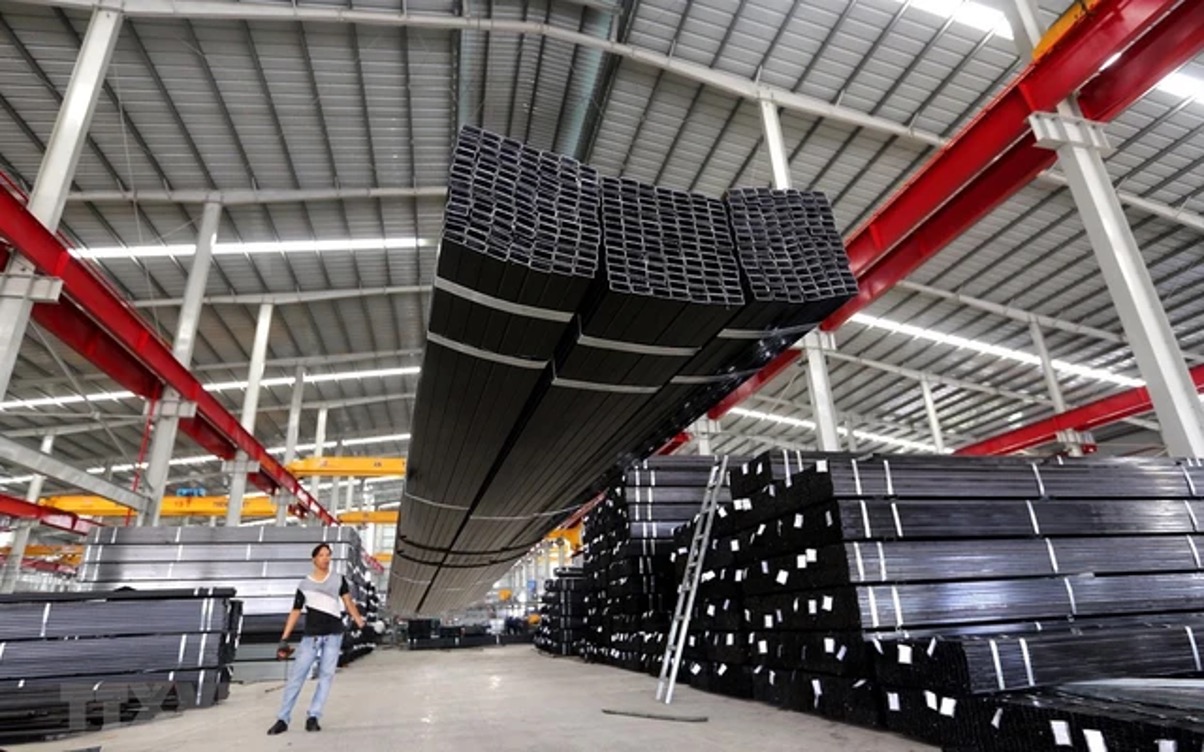

Aluminum extrusion brings many advantages to construction projects
The disadvantages of aluminum extrusion include:
Both aluminum extrusion and cast aluminum production processes have their distinct advantages and some limitations. Depending on the specific needs and applications of each type of aluminum, you can choose the appropriate aluminum production process for your project. Below is a detailed comparison between aluminum extrusion and cast aluminum.
| Criteria | Aluminum Extrusion | Cast Aluminum |
| Shape | Diverse but limited to cross-sectional profiles. | Complex shapes. |
| Size | Limited in size compared to the initial billet. | Larger than the initial billet. |
| Hardness | Very high with hardening measures. | Lower and more prone to porosity if air is trapped. |
| Surface | Smooth and fine. | Rough with imperfections. |
| Mold Benefits | Quick mold making and production. | Expensive and time-consuming. |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable and flexible. | Low, requiring significant time and cost. |
| Cost | Less expensive, suitable for quick production. | Expensive, suitable for long production runs. |
Aluminum alloys such as 6005, 6061, and 6063 have proven to have good heat treatment capabilities, effective electrical conductivity, and high wear resistance, even when placed in harsh environmental conditions. These aluminum billets are produced annually in large quantities to serve various applications such as aluminum frame doors, industrial component manufacturing, high-rise building construction, and heat sink production.
The technical standards for aluminum extrusion products are usually defined based on the chemical and mechanical properties of the alloys, such as 6005, 6061, and 6063. This ensures that the final product meets the desired quality and performance standards. Below is a table of the chemical composition and mechanical property standards for the mentioned alloys:
| Aluminum Grades | Si | Mg | Mn | Cu | Fe | Cr | Zn | Ti | Impurities | Al | |
| Individual | Total | ||||||||||
| 6005 | 0,5÷0,9 | 0,4÷0,7 | ≤0,5 | ≤0,3 | ≤0,35 | ≤0,3 | ≤0,2 | ≤0,1 | ≤0,05 | ≤0,15 | Remainder |
| 6061 | 0,4÷0,8 | 0,8÷1,2 | ≤0,15 | 0,15÷0,4 | ≤0,7 | 0,04÷0,35 | ≤0,25 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,05 | ≤0,15 | Remainder |
| 6063 | 0,2÷0,6 | 0,45÷0,9 | ≤0,1 | ≤0,1 | ≤0,35 | ≤0,1 | ≤0,1 | ≤0,1 | ≤0,05 | ≤0,15 | Remainder |
The physical and mechanical property requirements of alloys 6005, 6063, and 6061 are as follows:
| Alloy | Heat Treatment | Thickness at Measuring Point (mm) | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) | Elongation (%) | Hardness | |
| A50mm | A | Hw | |||||
| 6005 | T5 | ≤ 8 | ≥ 250 | ≥ 200 | – | ≥ 8 | ≥ 9 |
| T6 | ≤ 5 | ≥ 270 | ≥ 225 | ≥ 6 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 10 | |
| Over 5 to 10 | ≥ 260 | ≥ 215 | ≥ 6 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 12 | ||
| Over 10 to 25 | ≥ 250 | ≥ 200 | ≥ 6 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 12 | ||
| 6061 | T5 | ≤ 6 | ≥ 240 | ≥ 205 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 7 | ≥ 12 |
| T6 | ≤ 6 | ≥ 265 | ≥ 245 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 7 | ≥ 14 | |
| Over 6 | ≥ 260 | ≥ 240 | ≥ 10 | – | ≥ 14 | ||
| Alloy | Heat Treatment | Thickness at Measuring Point (mm) | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) | Elongation (%) | Hardness | |||
| A50mm | A | Min Thickness at Measuring Point (mm) | HV5 | Hw | |||||
| 6063 | T5 | ≤ 12 | ≥ 150 | ≥ 110 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 7 | ≥ 0,8 | ≥ 58 | ≥ |
| Over 12
to 25 |
≥ 145 | ≥ 105 | ≥ 8 | ≥ 7 | |||||
| T6 | ≤ 3 | ≥ 205 | ≥ 170 | ≥ 8 | – | – | – | ≥ 12 | |
| Over 3 to 25 | ≥ 205 | ≥ 170 | ≥ 10 | – | – | – | ≥ 12 | ||
In this context:
Series 7000 aluminum alloys have always been highly regarded since aluminum was first used in daily life. They are characterized by high strength, self-hardening and self-recovery of mechanical properties, creating reliability and superior performance. In this product range, aluminum alloys such as 7020, 7005, and 7003 are commonly used for rail bar rolls or welded structures, meeting demands in various industrial and construction applications.
Aluminum alloys in series 2000 and series 7000, known for their high strength, are particularly valued for their machinability and mechanical properties, especially among commonly used alloys for extrusion. Types such as 2014, 2024, and 2017 in series 2000, and 7075, 7021 in series 7000 fall into this category. They are typically used in aircraft structures and manufacturing technology, though they are rarely used in welding due to their relatively poor quality in this regard.
Non-heat-treatable alloys in series 3000 and extruded alloys in series 5000 are known for their good mechanical properties and high wear resistance. However, they are limited in workability, so extruded aluminum products often have simple shapes. Their common applications include road signs, boats, decorative items, architectural applications, and cold containers.
Overall, there are four main types of aluminum alloys used for the extrusion method introduced by Stavian Industrial Metal.
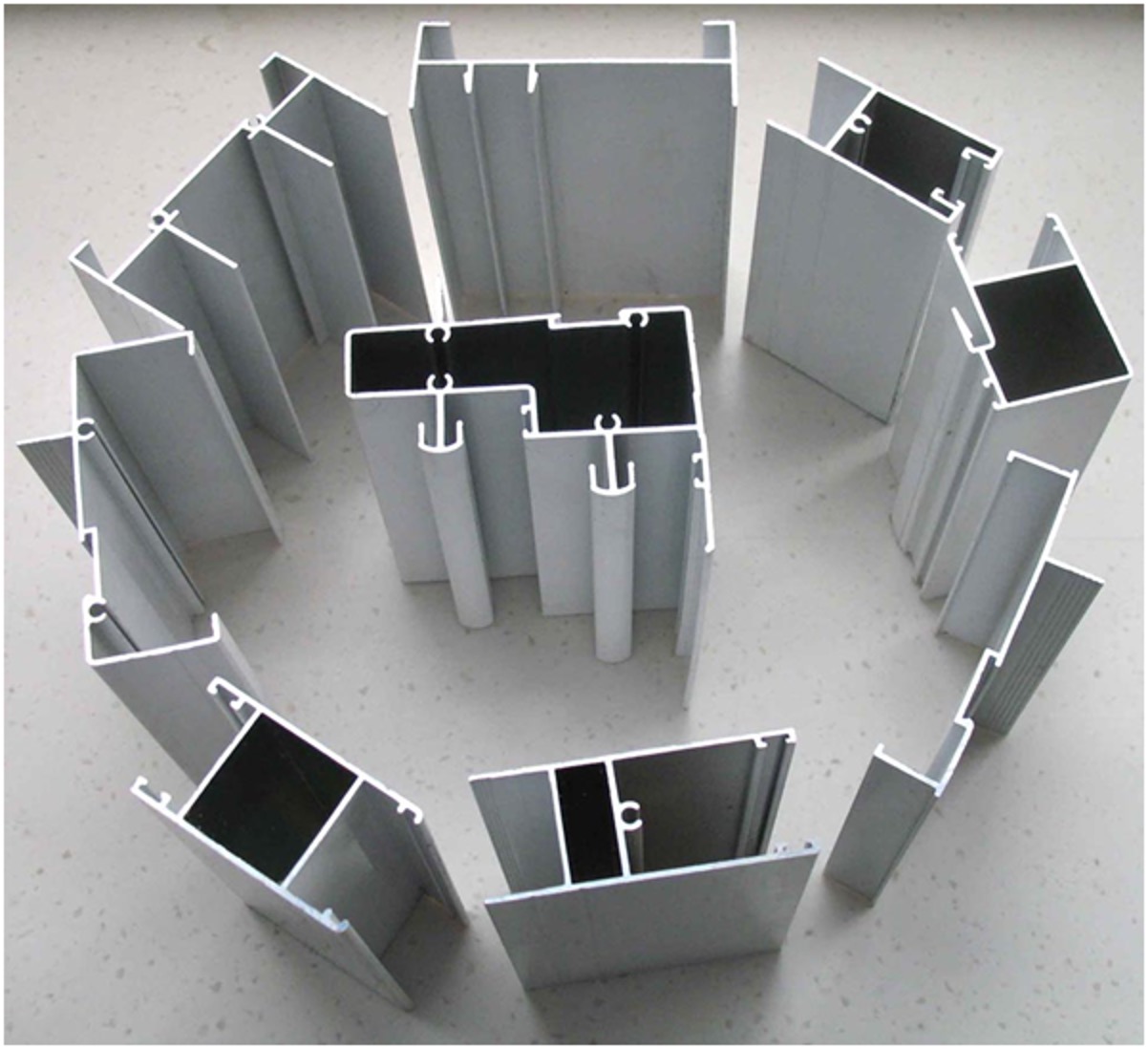
Aluminum extrusion is a flexible material capable of withstanding various pressures and can be shaped into many different forms to suit specific applications. Here are the common shapes that extruded aluminum can be manufactured into:
Additionally, extruded aluminum can be made into various other shapes like round tubes, oval shapes, channels, Z-profiles, T-profiles, H-profiles, I-beams, L-profiles, and many other forms depending on specific application requirements. This demonstrates the versatility and diversity of extruded aluminum in many industrial and construction fields.
Several factors affect the quality of extruded aluminum products, including:
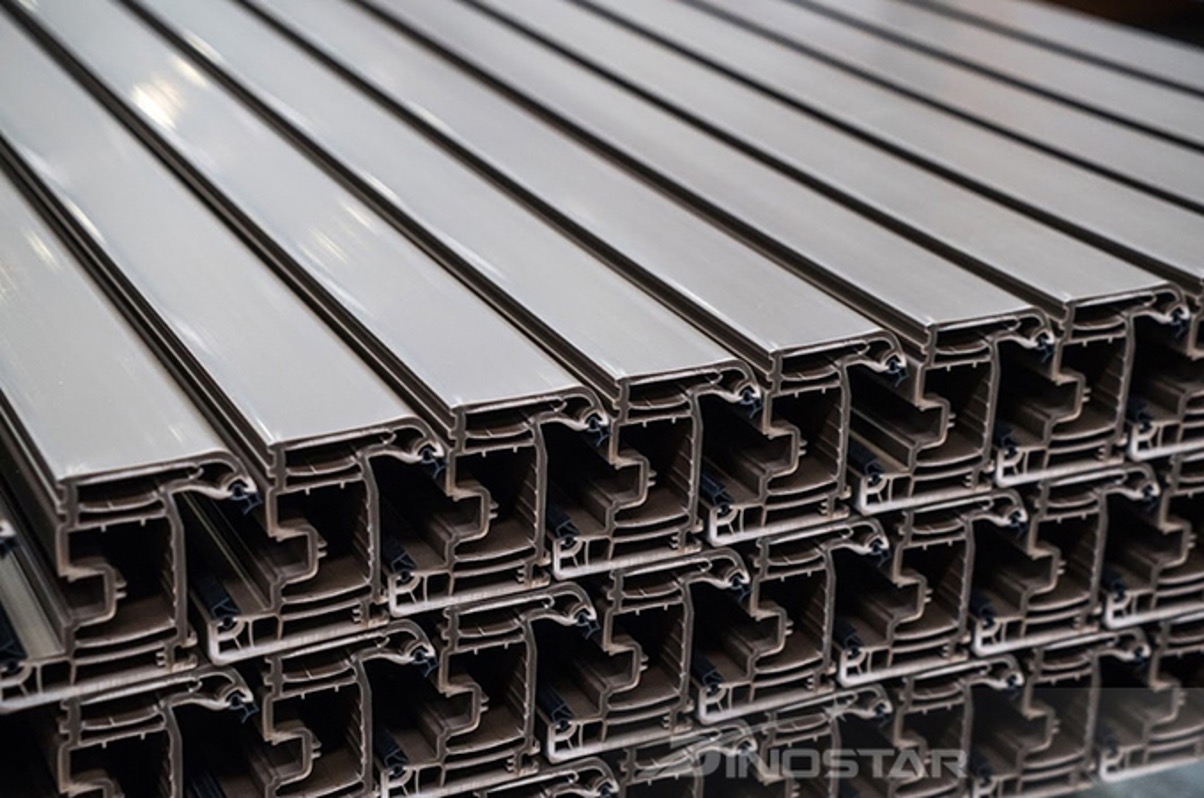

Có nhiều yếu tố quan trọng ảnh hưởng đến chất lượng của sản phẩm nhôm đùn
Extruded aluminum is widely used in various fields due to its superior properties in terms of durability, thermal, and electrical conductivity. Here are the main applications of extruded aluminum:
Stavian Industrial Metal is one of the leading suppliers of high-quality extruded aluminum. With the mission of providing customers with standard aluminum products that meet all usage requirements, Stavian Industrial Metal always prioritizes product quality.
Stavian Industrial Metal’s manufacturing facility is equipped with modern production lines, ensuring precise and efficient production processes. The experienced technicians at Stavian Industrial Metal are always ready to advise and assist customers in selecting suitable products.
Customers who choose to purchase extruded aluminum from Stavian Industrial Metal are guaranteed the best product quality. Careful selection of raw materials and stringent production control ensure that the final products meet the highest standards.
Reference
With a commitment to competitive pricing and professional after-sales service, Stavian Industrial Metal is confident in being a reliable partner for all projects involving extruded aluminum. For more detailed information and consultation, customers can visit Stavian Industrial Metal’s official website or contact directly.
Address
Website: https://stavianmetal.com
Email: info@stavianmetal.com
