Streamline your aluminum composite panel installation with this detailed, step-by-step guide. Learn the essential processes that experienced installers take to produce a flawless, long-lasting facade. From substrate preparation and framing to panel production, attachment, and weatherproofing, this comprehensive reference covers every important step. Discover skilled techniques for cutting, manipulating, and securing panels to achieve a consistent, visually spectacular finish. Learn about important safety precautions, expansion joint considerations, and maintenance requirements. Whether you’re a contractor, builder, or DIY enthusiast, this step-by-step guide will give you the confidence to take on any aluminum composite panel installation project and achieve professional-grade results.
Aluminum composite panels (ACPs), also known as aluminum composite materials (ACMs), are a type of sandwich panel construction that consists of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a lightweight core material.
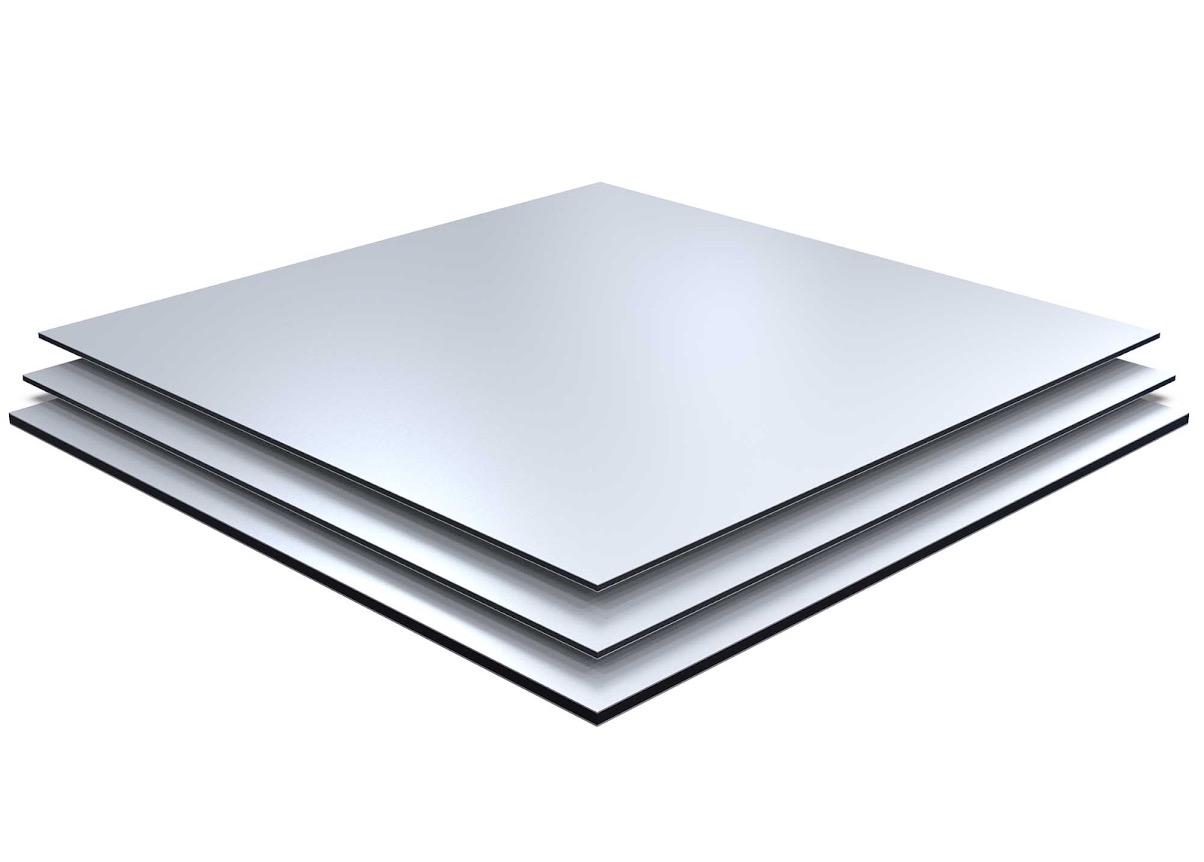
Here are the key details about aluminum composite panels:
Outer Layers: Two thin sheets of aluminum, typically 0.5mm to 0.8mm thick.
Core Material: A lightweight core, usually made of polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PU), or mineral wool.
ACP thickness can range from 3mm to 6mm, with 4mm being a common industry standard.
ACPs are available in a wide range of standard sizes, such as 1.22m x 2.44m, 1.52m x 3.05m, or custom sizes to suit specific project requirements.
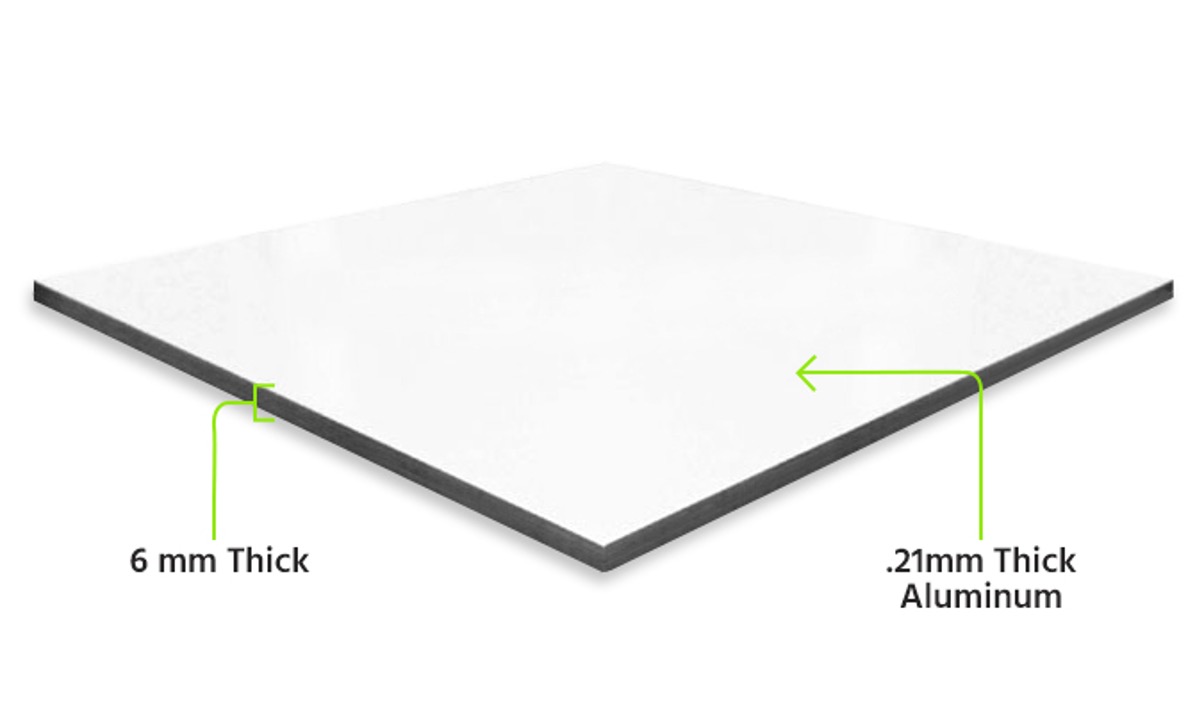
Aluminum sheets can be finished in a variety of ways, including anodized, PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) coated, or painted in a wide range of colors.
The finish choice can impact the panel’s appearance, durability, and maintenance requirements.
Polyethylene (PE) core: Offers good thermal insulation and is cost-effective, but has a lower fire rating.
Polyurethane (PU) core: Provides better thermal insulation and fire resistance compared to PE.
Mineral wool core: Offers the highest fire resistance and non-combustible properties.
Lightweight: Aluminum composite panels are significantly lighter than solid aluminum panels, making them easier to handle and install.
Rigidity: The sandwich construction provides excellent structural stability and rigidity.
Thermal Insulation: Dependent on the core material, aluminum composite panels can offer varying degrees of thermal insulation.
Weather Resistance: The aluminum outer layers provide excellent resistance to weathering, UV exposure, and corrosion.
Exterior Cladding: Aluminum composite panels are widely used for building facades, curtain walls, and soffits.
Interior Walls: They can be used for partitions, column cladding, and other interior applications.
Signage and Wayfinding: Aluminum composite panels are a popular choice for signage, displays, and various architectural features.
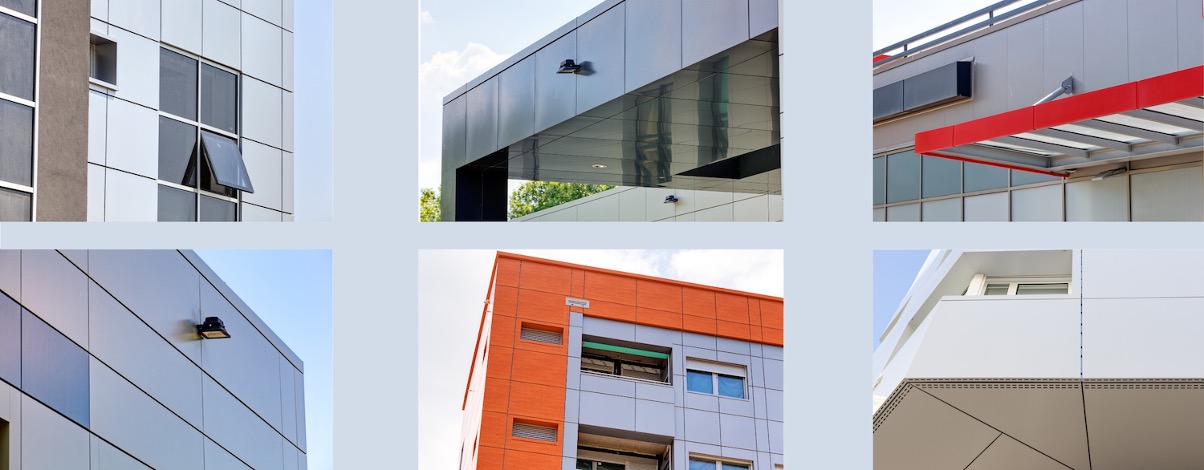

Understanding the aluminum composite panel details, including their composition, sizes, finishes, and performance characteristics, is crucial for specifying, designing, and installing these versatile construction materials.
Before installing aluminum composite panels (ACPs), there are several important factors to consider. Here are the essential things you should know:
Understand the different core materials used, such as polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PU), or mineral wool, as they have varying properties and performance characteristics.
Ensure the selected panels meet the required fire safety and building code regulations for the specific application.
Assess the structural integrity of the underlying wall or substrate to ensure it can adequately support the weight of the aluminum composite panel system.
Determine the appropriate framing and attachment methods required for a secure and stable installation.
ACPs can expand and contract owing to temperature changes, therefore expansion joints and enough clearances are required to accommodate this movement.
As a result, structural rivets must be installed outside. The stem diameter should be 5mm, with the rivet head diameter ranging from 11mm to 14mm. When riveting aluminum composite panels, it is recommended that the panel be fixed in order from the middle to both ends, and because the panel will expand and contract with temperature changes, the aperture above the composite panel should be about 1 mm larger than the diameter of the rivet to ensure the panel’s flatness.
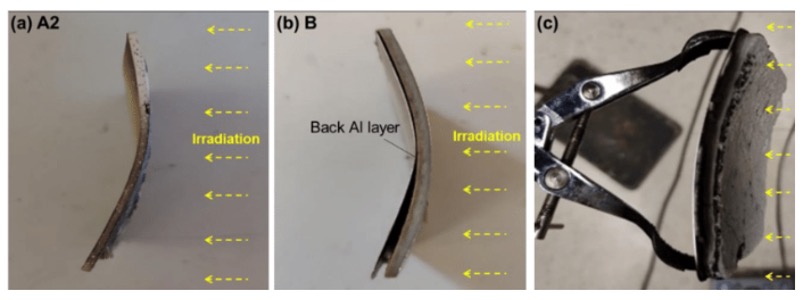
Improper installation can lead to warping, bulging, or cracking of the panels.
Ensure appropriate sealing and flashing around panel edges, corners, and penetrations to prevent water infiltration and keep the assembly weathertight.
Consider using sealants, gaskets, and other accessories to build a strong and long-lasting weather barrier.
Rubber operations should not be carried out on wet days. The silicon germanium weatherproof adhesive should be filled to full capacity and applied in an area with temperatures ranging from 15°C to 30°C and relative humidity levels of 50% or higher.
Provide adequate air circulation and drainage behind the aluminum composite panel system to prevent moisture buildup and potential issues like mold or corrosion.
Incorporate ventilation channels, weep holes, and other design features to promote proper airflow and water management.
Develop a regular maintenance plan to clean the aluminum composite panel surfaces and address any potential issues, such as dirt accumulation or minor damage.
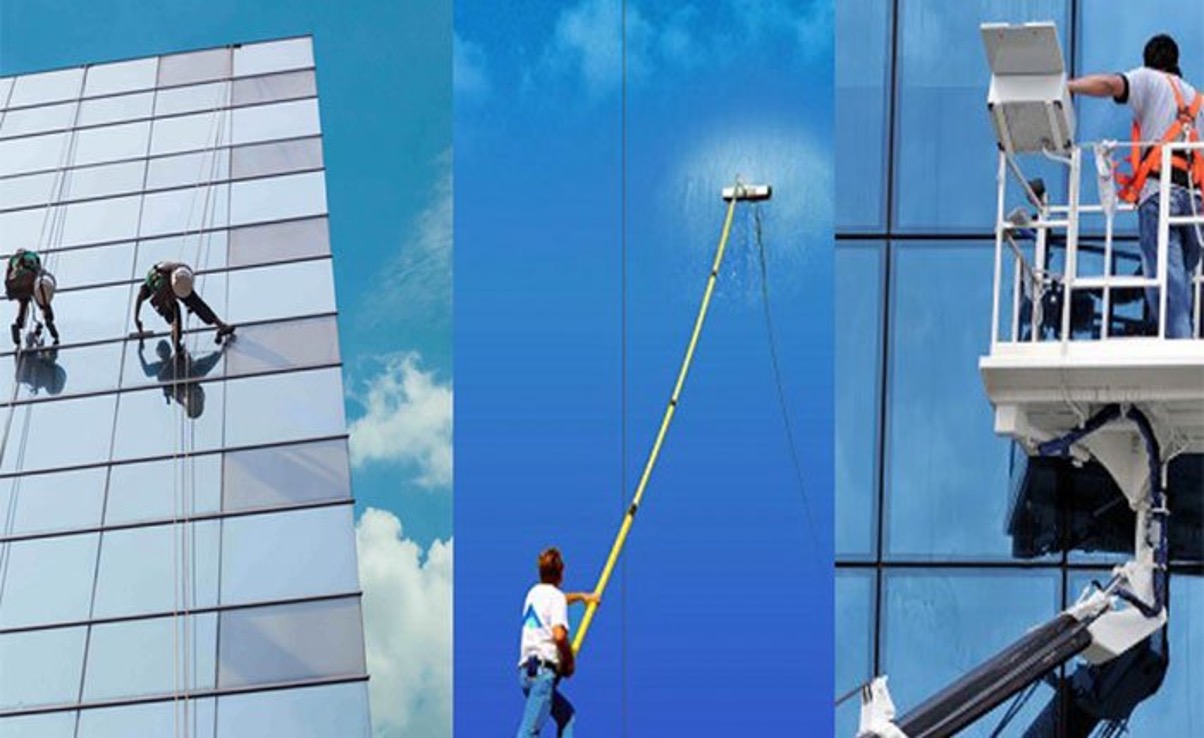

Proper cleaning techniques and the use of recommended cleaning products can help preserve the appearance and performance of the panels over time.
By addressing these key considerations during the planning and installation stages, you can ensure the long-term performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal of your aluminum composite panel application.
The aluminum composite panel installation details typically involves the following steps:
Inspect the wall or substrate surface to ensure it is clean, dry, and free of any irregularities or defects that could affect the panel installation.
Evaluate the structural integrity of the substrate and determine if any reinforcement or modifications are required to support the weight of the ACP system.
If necessary, install a secondary framing or furring system to create a level and uniform surface for the panel attachment.
Determine the appropriate framing system, which may include metal studs, aluminum extrusions, or a combination of both.
Install the framing members vertically, spaced according to the panel dimensions and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Ensure the framing is plumb, level, and securely anchored to the underlying substrate.
Incorporate any necessary expansion joints, clearances, and attachment points for the ACP system.
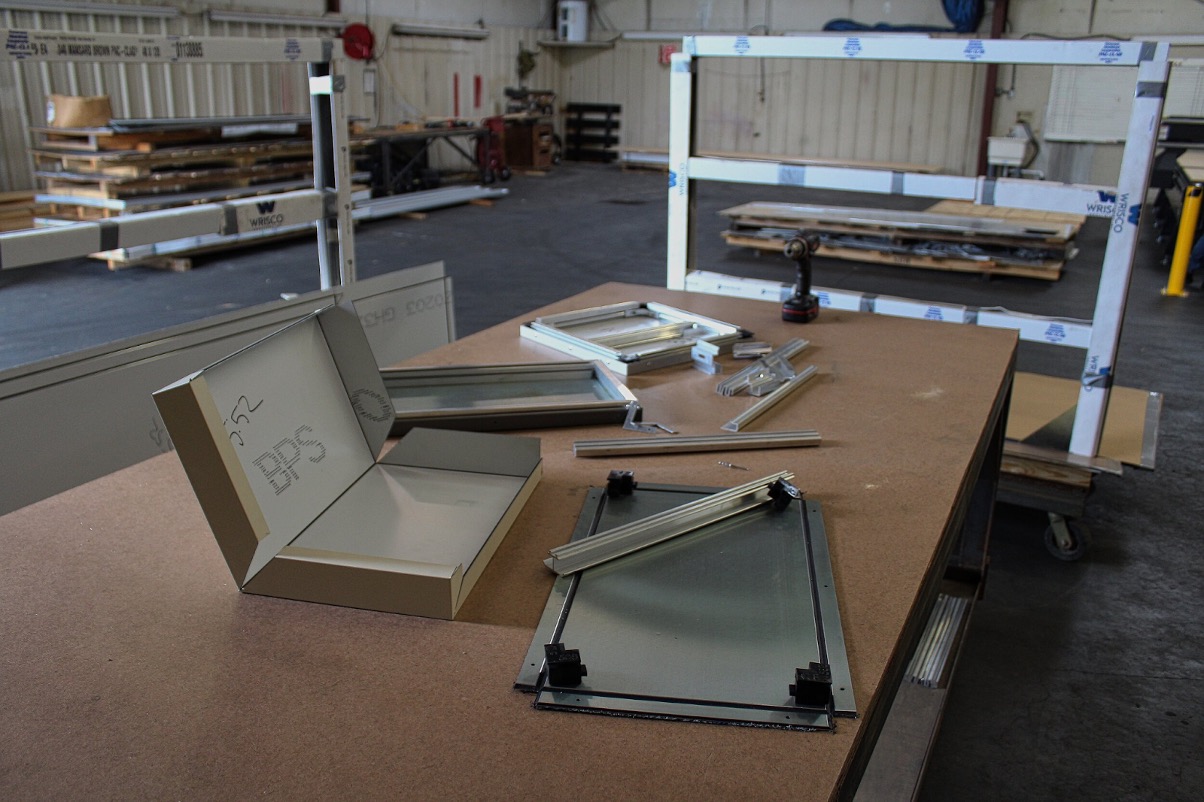

Measure the wall or facade dimensions and create a detailed cutting plan for the ACP sheets.
Use a precision saw or table saw to cut the panels to the required sizes, taking care to protect the panel surfaces during the cutting process.
Create any necessary cutouts, openings, or edge details to accommodate windows, doors, electrical boxes, or other building components.
Label the panels to ensure proper identification and placement during installation.
Lift and position the ACP sheets onto the prepared substructure, aligning them carefully with the framing members.
Secure the panels to the framing using the appropriate fasteners, such as rivets, screws, or concealed clip systems.
Ensure the fasteners are properly spaced and installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications to provide a secure and stable attachment.
Allow for the required expansion gaps around the panel edges to accommodate thermal movement.
Apply high-quality sealants, gaskets, or compression seals along the panel edges, corners, and any penetrations to create a watertight barrier.
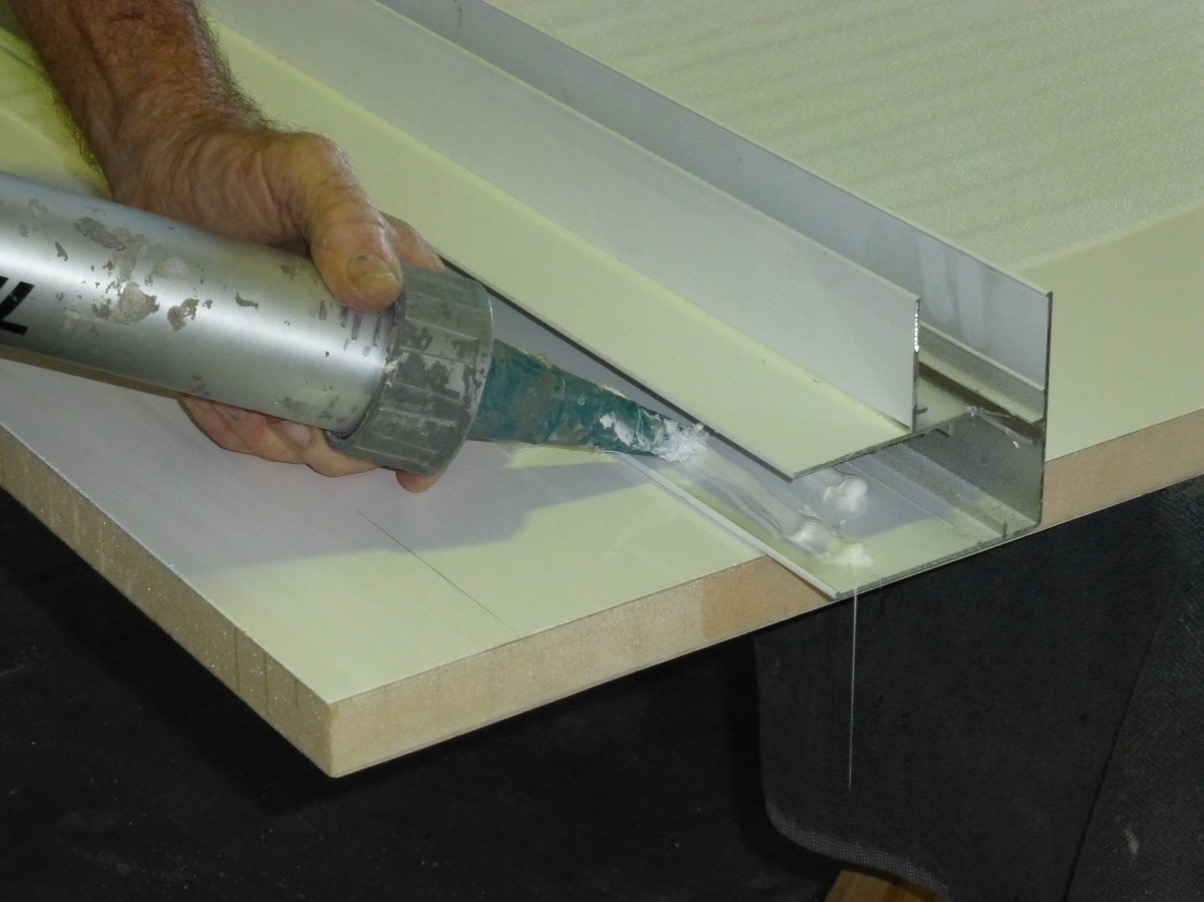

Install any necessary flashing, weep holes, or ventilation channels to manage water drainage and air circulation behind the ACP system.
Ensure all sealant joints are tooled and smoothed to provide a professional appearance and effective seal.
Carefully inspect the installed ACP system for any gaps, misalignments, or defects, and address them as necessary.
Clean the panel surfaces using the manufacturer-recommended cleaning agents and methods to remove any construction debris or residue.
Apply any required touch-up paint or sealant to maintain the desired aesthetic and protect the panels.
Establish a regular maintenance schedule to clean and inspect the ACP system, addressing any potential issues that may arise over time.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended cleaning and maintenance procedures to ensure the long-term performance and appearance of the panels.
Maintain proper documentation of the installation, including panel specifications, fastener details, and any warranty information.
Proper planning, attention to detail, and adherence to the manufacturer’s installation guidelines are crucial for ensuring the successful and reliable installation of aluminum composite panels.

By following the detailed, step-by-step installation procedure outlined in this guide, you can ensure a successful and high-quality aluminum composite panel project. Remember, each phase of the process, from substrate preparation to final weatherproofing, plays a crucial role in the overall performance and longevity of the facade. Attention to detail, adherence to manufacturer guidelines, and proper planning are key to achieving a seamless, professional-looking finish. Regularly maintaining and inspecting the aluminum composite panel system will also help preserve its aesthetic and structural integrity for years to come. With the knowledge and confidence gained from this comprehensive step-by-step guide, you’re well-equipped to tackle any aluminum composite panel installation with ease and assurance.
Address
Website: https://stavianmetal.com
Email: info@stavianmetal.com
