Discover everything you need to know about CRC steel, including its price and quality, in this comprehensive guide. Explore the properties, applications, and benefits of CRC steel, a reliable and durable material used in various industries. Gain valuable insights into the factors that influence CRC steel prices and market trends. Whether you’re a buyer, manufacturer, or industry professional, this article provides valuable information to help you make informed decisions. Stay updated on the latest developments in CRC steel pricing and understand how it impacts the overall quality and cost-effectiveness of your projects.
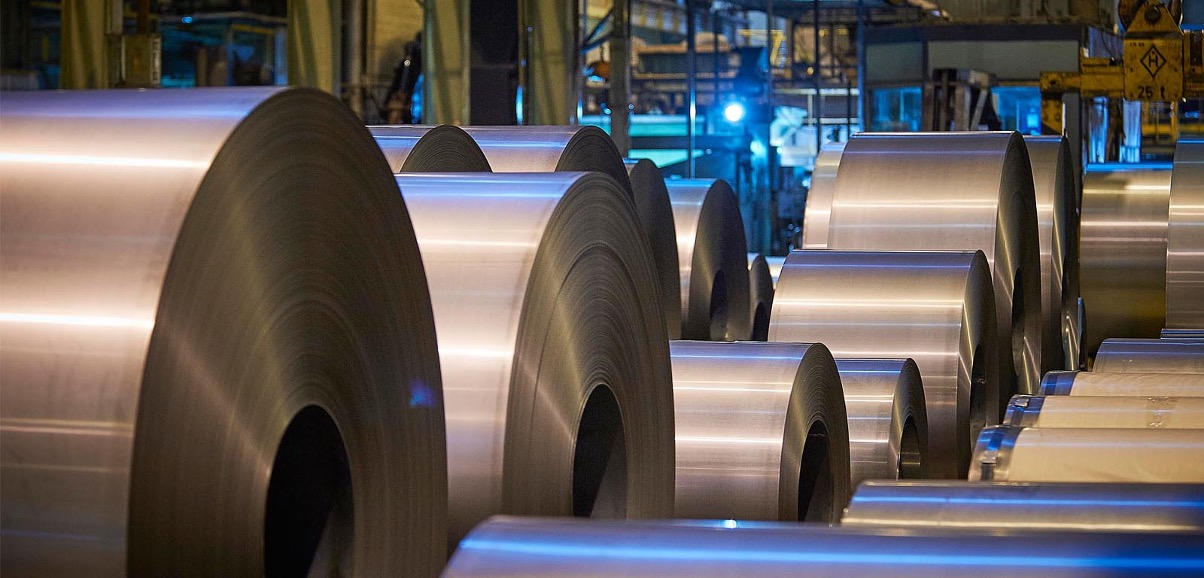

CRC steel stands for Cold Rolled Coils or Cold Rolled Steel. It refers to a type of steel that has undergone a cold rolling process. Cold rolling is a method of reducing the thickness of steel by passing it through a series of rollers at room temperature. This process results in a smoother surface finish and tighter dimensional tolerances compared to hot-rolled steel.
CRC steel is known for its excellent surface quality, uniform thickness, and enhanced mechanical properties. It typically has higher strength and hardness compared to hot-rolled steel. The cold rolling process also improves the flatness and straightness of the steel, making it suitable for applications that require precision and a high-quality surface finish.
CRC steel, which stands for Cold Rolled Coils, exhibits specific technical specifications that can vary based on the grade, standard, and manufacturer. The chemical composition of CRC steel generally consists of low carbon content to ensure good formability, along with elements such as manganese to enhance strength and formability. Phosphorus and sulfur are typically limited to maintain good surface quality, while small amounts of silicon may be present to improve surface finish.
In terms of mechanical properties, CRC steel exhibits a range of characteristics. Tensile strength, which measures the resistance of the steel to breaking under tension, generally falls between 270 MPa and 590 MPa, depending on the specific grade. Yield strength, the amount of stress required to deform the steel plastically, varies based on the grade and thickness. Elongation, a measure of the steel’s ability to stretch before fracturing, typically falls in the range of 26% to 50%, with exact values dependent on the grade and thickness. Hardness, which indicates the steel’s resistance to indentation or scratching, can differ based on the grade and processing conditions.
CRC steel also has dimensional tolerances that ensure uniformity. The thickness of CRC steel typically ranges from 0.4mm to 3.0mm, though it can be customized to meet specific requirements. The width of CRC steel coils can range from 600mm to 2000mm, accommodating various applications and customer specifications. Length is determined based on customer requirements.
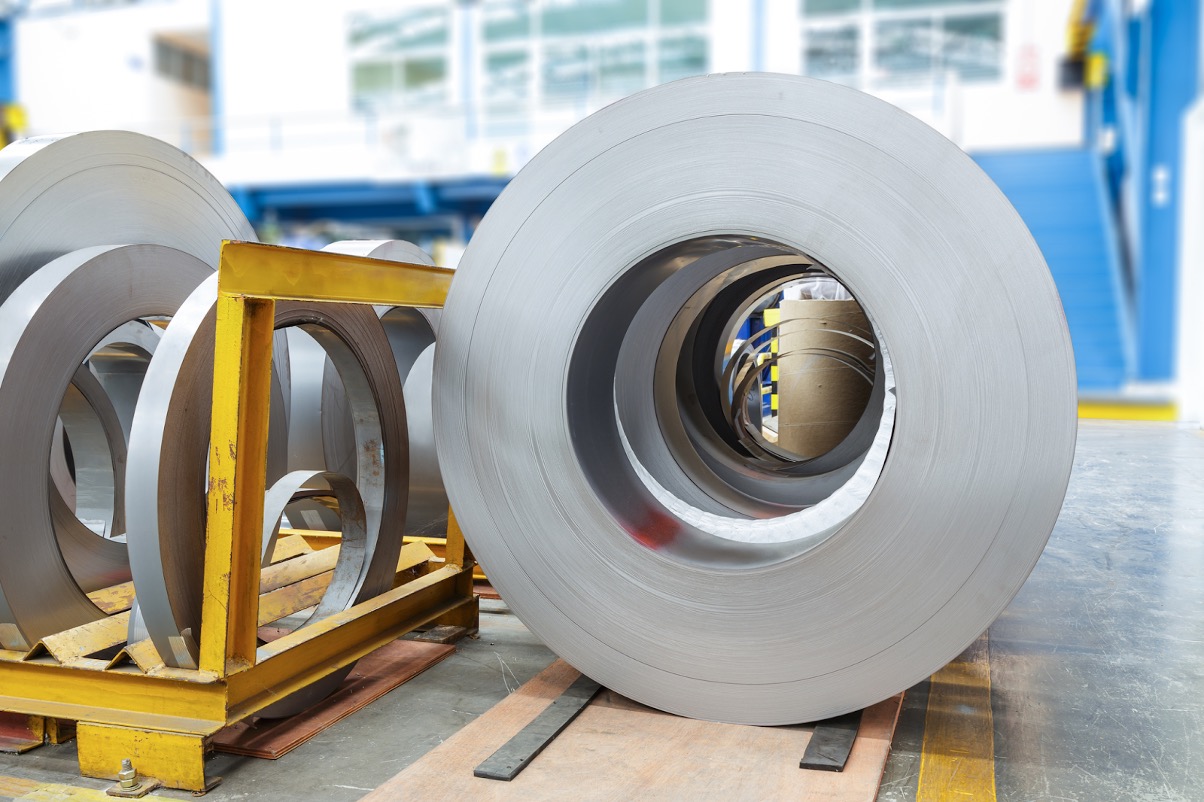

With regard to surface finish, CRC steel undergoes a cold rolling process that imparts a smooth surface. The finish can be either bright or matte, depending on the specific needs and preferences of the application. Additionally, CRC steel can be further coated or treated to enhance its corrosion resistance or improve its surface properties. Common treatments include galvanizing, oiling, or passivation.
It’s important to note that the precise technical specifications of CRC steel can vary depending on the grade, standard, and manufacturer. For accurate and detailed information, it is advisable to refer to the product’s technical data sheet or consult with the supplier, who can provide specific details of a particular grade of CRC steel.
The application of CRC steel (Cold Rolled Coil steel) is diverse and widespread across various industries. Here are some common applications of CRC steel:
Overall, CRC steel’s properties, such as uniform thickness, excellent surface finish, formability, and strength, make it suitable for diverse applications across industries ranging from automotive and construction to appliances, furniture, and general manufacturing.
Cold rolled steel prices in January 2024
The price of CRC steel (Cold Rolled Coils) can be influenced by various factors. Here are some key factors that can impact the pricing of CRC steel:
Raw Material Costs: The cost of the raw materials used in the production of CRC steel, such as hot-rolled steel coils, plays a significant role in determining the price. Fluctuations in the prices of iron ore, coal, and other raw materials can directly affect the overall cost of production and, consequently, the price of CRC steel.

Economic Conditions: Economic factors, such as overall economic growth, industrial production levels, and construction activity, can influence the demand for CRC steel. During periods of economic expansion and increased construction activity, the demand for CRC steel typically rises, potentially leading to higher prices. During an economic slump, demand may decline, resulting in cheaper pricing.
Trade Policies and Tariffs: Government policies, including import/export restrictions, tariffs, and trade agreements, can impact the price of CRC steel. Changes in these policies can affect the availability of CRC steel in the market and may result in price fluctuations.
Market Demand and Supply: The balance between the demand and supply of CRC steel in the market can impact its price. If the demand for CRC steel is high and supply is limited, prices tend to increase. Conversely, if the demand is low and supply is abundant, prices may decrease.

Energy Costs: The cost of energy, including electricity and fuel, can impact the production costs of CRC steel. Fluctuations in energy prices can influence the overall cost of manufacturing and, consequently, the pricing of CRC steel.
Currency Exchange Rates: For international trade, currency exchange rates can affect the price of CRC steel. Currency fluctuations can impact the cost of imported raw materials or influence the competitiveness of exported CRC steel, ultimately affecting the pricing dynamics.
Production and Operating Costs: The cost of production, including labor, equipment, maintenance, and overhead expenses, can contribute to the price of CRC steel. Changes in these production and operating costs can influence the final pricing of the product.
These factors can interact and vary over time, leading to fluctuations in the price of CRC steel. Additionally, regional and market-specific factors may also have an impact on pricing.
HRC (Hot Rolled Coils) steel and CRC (Cold Rolled Coils) steel are two distinct forms of steel produced through different manufacturing processes. Here are the main differences between HRC and CRC steel:
HRC Steel: Hot rolled steel is produced by heating steel billets or slabs above their recrystallization temperature, typically around 1100 to 1300 degrees Celsius. The heated steel is then passed through a series of rolling mills, where it is continuously squeezed and shaped into its final thickness and width. The high temperature during the rolling process makes the steel easier to shape, but it also results in a rough surface texture.
CRC Steel: Cold rolled steel is produced by taking hot rolled coils and subjecting them to a cold reduction process. The hot rolled coils are first pickled to remove any scale or surface impurities. Then, they are passed through a series of rolling mills at room temperature, where the thickness of the steel is reduced. The cold rolling process imparts better dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and higher mechanical properties to the steel compared to hot rolled steel.

HRC Steel: Hot rolled steel has a characteristic scaled and rough surface due to the formation of an iron oxide layer known as mill scale. The mill scale is a dark, rough, and flaky oxide layer that forms during the high-temperature rolling process. The rough surface texture of HRC steel makes it suitable for applications where aesthetics are not a primary concern.
CRC Steel: Cold rolled steel has a smoother and more refined surface finish compared to hot rolled steel. The cold rolling process removes the mill scale and other surface imperfections, resulting in a cleaner and relatively smooth surface. The improved surface finish of CRC steel makes it suitable for applications where appearance and surface quality are important.
HRC Steel: Hot rolled steel exhibits higher ductility and toughness compared to cold rolled steel. The high temperature during the rolling process allows the steel to undergo significant plastic deformation, resulting in higher elongation and lower yield strength. HRC steel is often preferred in applications where formability and flexibility are required, such as in structural components and welding/fabrication.
CRC Steel: Cold rolled steel generally has higher hardness and strength compared to hot rolled steel. The cold rolling process work-hardens the steel, which increases its strength and hardness. Cold rolled steel has a lower elongation and higher yield strength compared to hot rolled steel. The higher strength and hardness of CRC steel make it suitable for applications that require enhanced mechanical properties, such as automotive parts and electrical components.
HRC Steel: Hot rolled steel coils may have some variations in thickness and width due to the rolling process. The dimensional tolerances for HRC steel are generally not as tight as those for cold-rolled steel.
CRC Steel: Cold rolled steel coils have tighter dimensional tolerances compared to hot rolled steel. The cold rolling process allows for better control over the thickness, width, and length of the steel, resulting in more precise and consistent dimensions.
HRC Steel: Hot rolled steel finds application in various industries and sectors. It is commonly used in structural components, such as beams and columns, as well as in welding and fabrication processes. HRC steel is also utilized in the production of pipes, railway tracks, and general engineering applications.
CRC Steel: Cold rolled steel is often preferred in applications that require a smooth surface finish, precise dimensions, and higher strength. It is commonly used in automotive parts, such as body panels and chassis components, as well as appliances, construction materials, electrical components, and furniture.

Both HRC and CRC steel have their specific advantages and applications based on their unique properties. The selection of the appropriate type of steel depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the application, desired surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties needed for the end use. Consulting with steel manufacturers, suppliers, or industry experts can provide further guidance on selecting the most suitable type of steel for a particular application.
In conclusion, CRC steel is a crucial material with a wide range of applications across industries. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have delved into its properties, applications, and the factors influencing its price. CRC steel offers reliability, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for various projects. Understanding the market trends and pricing dynamics is essential for making informed decisions. By staying updated on CRC steel prices, you can optimize your procurement strategies and ensure cost-effectiveness without compromising on quality. Whether you’re involved in construction, manufacturing, or engineering, this knowledge empowers you to leverage the benefits of CRC steel in your projects, maximizing value and performance.
Address
Website: https://stavianmetal.com
Email: info@stavianmetal.com
