| Categories | Details |
| Type | H, U, I, W beam, EA… |
| Standard | JIS, ASTM, KS, BS, EU… |
| Grade | SS400, SS490, A36, A572… |
Section Steel
Stavian Industrial Metal provides a full range of section steel including H beam, equal-leg angles from famous factories like POSCO YAMATO, TISCO, An Khanh Steel…
The products are produced on modern lines according to international standards such as JIS G3192:2014, KS D3502:2021, ASTM A6-11, BS 4-1:2005, EN 10365:2017…
0 ₫
Section steel is one of the most commonly used types of steel in the construction industry. With their high strength and good load-bearing capabilities, steel sections play a crucial role in various fields such as design, engineering, science, and industrial applications. So, what is the concept of steel sections? How is this type of steel produced? Let’s explore the details in the following article with Stavian.
Read more: Table of I, C, U Steel Sections
What is section steel?
Section steel, also known as structural steel, is a type of steel material with shapes resembling letters such as H, V, I, L, and more. This type of steel plays a significant role in various industries, including construction, shipbuilding, bridge construction, broadcasting towers, machinery transportation, container frame fabrication, warehouse storage racks, industrial boilers, pre-engineered building structures, foundation piles for industrial buildings, and factory construction.
Types of section steel commonly used today
Steel sections are currently categorized into various shapes and sizes. Below are details of some types of steel sections:
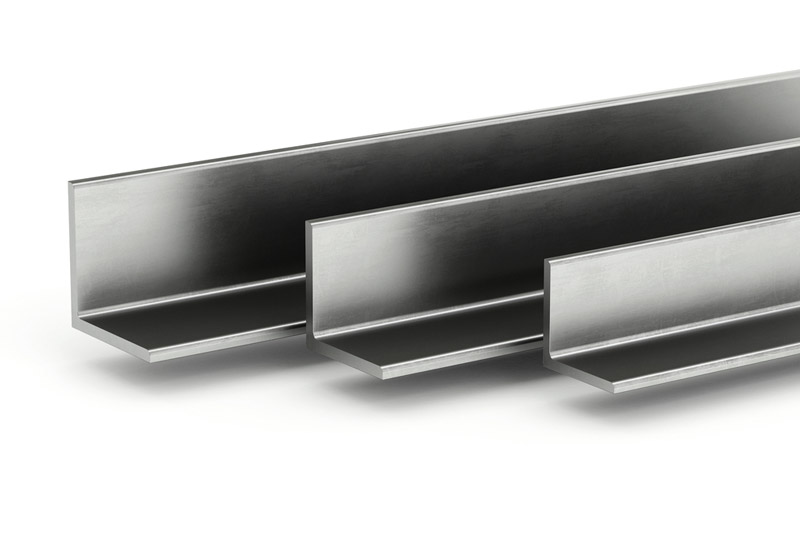
L-section steel beam
L-section steel beams have a cross-sectional shape resembling the letter “L.” They are known for their high rigidity, strong load-bearing capacity, and excellent corrosion resistance, especially when galvanized. Standard dimensions for L-section steel beams typically range as follows:
- Height: 100 – 900 mm
- Flange width: 55 – 300 mm
- Length: 6000 & 12000 mm
V-shaped angle steel
V-shaped angle steel is characterized by its rigidity, high load-bearing capacity and strength. These steel sections are also known for their resistance to environmental factors like temperature and humidity, making them ideal for use in the construction and shipbuilding industries. Some types of V-shaped angle steel include V 100, V 80, V 70, V 256, L-V 200, V 175, V 150, V 130, V 53, V 50, V 45, V 30.
U beams
U beams come in various sizes and can withstand high pressure. They have numerous applications in civil construction, including frameworks for vehicles, antenna towers, and interior design. Commonly used U-shaped steel sections include U50, U100, U200, U400, with standard specifications as follows:
- Horizontal width: 40 – 500 (mm)
- Flange height: 25 – 100 (mm)
- Lenght of a single U beam: 6000 – 12000 (mm)
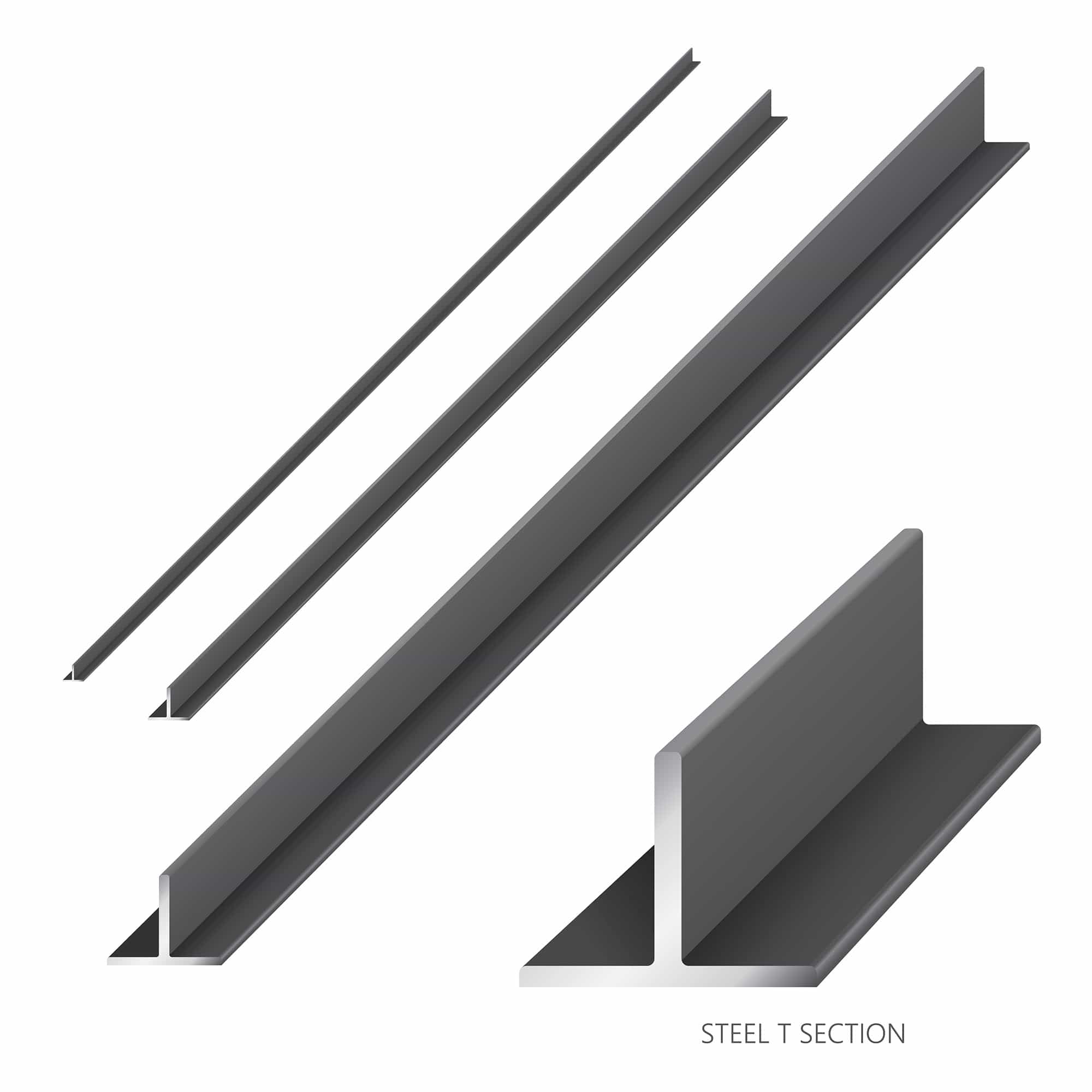
C-section steel
C-shaped steel sections, also known as C-channel, have a cross-sectional shape resembling the letter “C.” There are various types of C-shaped steel sections, such as black steel, galvanized steel, and hot-dip galvanized steel, each with distinct characteristics and applications.
I beams
I beams have a similar shape to H beams but with shorter flanges. They are known for their ability to withstand high pressure and are typically used in construction and various industrial applications.
H beams
H beams have a cross-sectional shape resembling the letter “H” and can withstand extremely high pressure. Common types of H beams include H100, H150, H300, with different sizes suitable for various industrial construction purposes.
Standard dimensions for H beams typically range as follows:
- Height 100 – 900 (mm)
- Flange width 50 – 400 (mm)
- Length 6000 – 12000 (mm)
Learn more: How much does section steel weigh?
Latest section steel standards
Section steel is an extremely important and widely used material in the construction industry. Therefore, ensuring quality relies on the following steel section standards:
Alloy proportions
Steel is an alloy composed of various elements, including iron, carbon, and other chemical elements. Changes in the proportions of these components significantly affect the properties of steel. Thus, controlling the proportions of elements during steel production is crucial.
Standard carbon content
The carbon content in section steel typically ranges from 0.02% to 2.14% by weight. Variations in carbon content influence steel’s flexibility and load-bearing capacity after the heating process. High carbon-content steel usually exhibits higher strength and load-bearing capacity, whereas low carbon-content steel tends to have lower strength and load-bearing capacity.
Other metal element content
Other elements, such as manganese (Mn), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), aluminum (Al), copper (Cu), also play a significant role in determining the properties of steel sections. Based on the ratios of these elements, alloy steel is divided into three categories: low-alloy steel, medium-alloy steel, and high-alloy steel, each with distinct applications in the construction industry.
Quality standards
In addition to carbon content and alloy composition, the quality of section steel depends on the proportions of other impurities like sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P). Regular quality steel typically contains 0.06% S and 0.07% P, while good quality steel has 0.035% S and 0.035% P. High-quality steel has 0.025% S and 0.025% P, and very high-quality steel features 0.025% P and 0.015% S.
Thickness
Each steel section manufacturer provides various thickness specifications, which are essential when selecting the right steel section for a specific project. Different steel section types have varying thicknesses to suit particular applications in the construction industry.
Rolling technology
The steel rolling technology also influences the quality of section steel. There are two common methods: hot rolling and cold rolling. Each manufacturer has its own rolling lines, impacting the characteristics of the final steel product.
Read more: U100 steel beam, I200 steel beam, H200 section steel
Section steel production process
In the construction industry, section steel plays an indispensable role. To ensure the quality and general characteristics of various steel sections, the production process must adhere to strict control steps. Here are the four main stages in the section steel production process:
Ore mining and processing – The initial stage
This crucial stage marks the beginning of the section steel production process. The original raw ore must undergo a series of tests and surveys to ensure it meets the necessary quality standards. The types of raw ore used for steel section production include iron ore pellets, iron ore, and sinter, along with supplementary materials like coke and limestone. A process involving these materials occurs in a blast furnace to create the necessary strength for the final product.
Creating molten steel
After the raw ore has been processed through the heating stage, molten metal will be generated. This molten stream will be directed into a furnace or electric arc furnace. Here, the molten metal will be separated and processed to eliminate impurities and achieve the desired chemical composition.
This is a crucial stage for determining the steel grade. Therefore, adjusting the chemical composition at this stage should be done carefully and in accordance with the specified ratios.
Casting into finished products
Next, to shape the steel, the molten metal is delivered to steel manufacturing plants. At these facilities, the molten metal will be transformed into three main types of billets: billets, slabs, and blooms.
- Billets: Used for creating various steel rolled sections, including equal angle steel with typical dimensions like 100×100, 125×125, 150×150.
- Slabs: Used to produce hot-rolled coil steel, steel plates, and various other steel sections. Slabs are commonly preferred in steel manufacturing plants.
- Blooms: A synthesis of both preceding types, blooms are used to manufacture construction steel, steel plates, and various diverse steel sections.
Rolling into finished products
The billets from stage 3 will have two states: hot and cold. They will be sent to steel production plants to be rolled into finished products.
- Hot billets will be continuously rolled at a high level to create robust and attractive steel products, including U, I, V, H, C, T-shaped steel sections, both with and without ribs.
- Cold billets need to be cooled to the appropriate temperature before rolling. They will then pass through a descaling line and later through a rolling mill with a series of continuous rolls. The number of rolls depends on the thickness of the hot-rolled coil and the required thickness of the final product.
Stavian Industrial Metal – A trusted provider of various steel sections in Vietnam
In the modern construction industry, many companies have emerged to meet the demands of Industry 4.0. However, not all brands provide steel section products of the same quality. Therefore, you need to find a reputable supplier to ensure the quality of your construction projects.
One such brand you can’t overlook when looking for a reliable material supplier is Stavian. With years of operation, the company consistently satisfies customers right from their initial impressions. They provide a variety of steel sections, including imported steel sections, standard-shaped steel, and more. The production process at Stavian undergoes rigorous quality control at each stage, ensuring the quality and quantity of products delivered to customers.
For more detailed information on steel section machining prices, don’t hesitate to get in touch with Stavian via the information below for quick support.
View more other products
Contact form