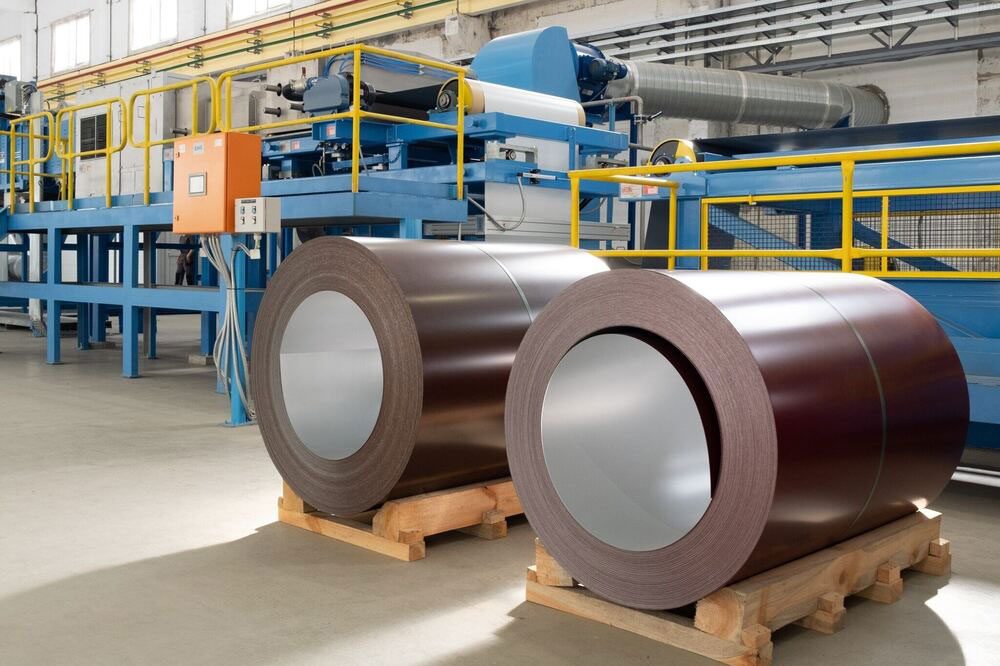
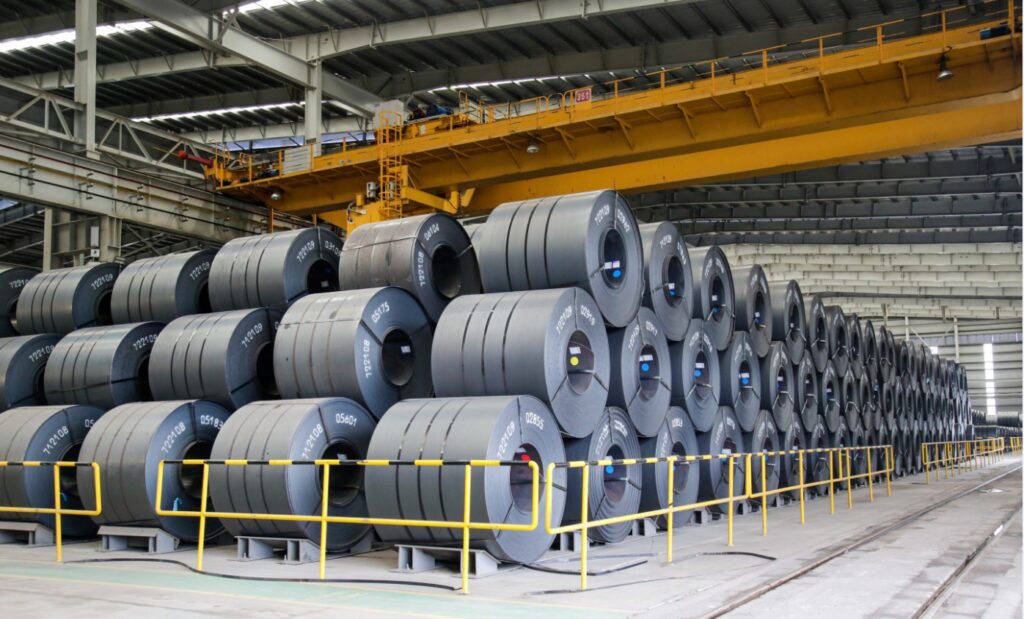
| Categories | Details |
| Coil | 0.2 – 6mm in thickness |
| Plate | Cut-to-order |
| Type | Cold rolled coil (CR), galvanized coil (CG), electromagnetic coil (ES), oil coated coil (PO), 2nd grade steel plates and coil… |
| Standard | JIS, ASTM, EN, JFS, AS… |
Cold Rolled Steel
Stavian Industrial Metal.,JSC provides a full range of cold rolled steel products in coils, plates, coils of galvanized, SPHC, SPCC…
Besides, we also supply sheet & coil products in first and second grade from big factories around the world such as Hyundai Steel, Nippon Steel,…
0 ₫
What is cold-rolled steel
Cold-rolled steel is an important material widely used in the industrial sector. It is a type of steel known for its flexibility, ease of processing, and relatively good corrosion resistance. Cold-rolled steel is manufactured through a specialized production and heat treatment process.
The production process of cold-rolled steel
Raw materials and alloy composition
Cold-rolled steel is typically made from primary materials such as iron and carbon. The alloy composition of cold-rolled steel can be adjusted to achieve the required properties, such as hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance.
The production process of cold-rolled steel
The production process for cold-rolled steel includes stages such as iron smelting, steelmaking, fabrication, and thin rolling. This process ensures the quality and uniformity of cold-rolled steel.
Processing and heat treatment in the manufacturing process
After cold-rolled steel is produced, it undergoes various processing and heat treatment steps to enhance its hardness and mechanical properties.

Cold-rolled steel standards
Cold-rolled steel is regulated and standardized by various organizations and standardization bodies worldwide. These standards ensure the uniformity and quality of cold-rolled steel throughout the manufacturing, processing, and usage stages. Below are some common standards for cold-rolled steel:
International standards:
- ASTM A1008/A1008M: The standard by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) for cold-rolled steel.
- EN 10130: The standard by the European Standardization Committee (EN) for cold-rolled steel.
National standards:
- JIS G3141: The standard by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) for cold-rolled steel.
- GB/T 5213: The standard by the Chinese National Standards (GB) for cold-rolled steel.
These standards specify requirements for the chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, and other characteristics of cold-rolled steel. For each standard, there may be various grades or classifications of cold-rolled steel, depending on the intended use and specific technical requirements.
Adhering to these standards ensures compatibility and interchangeability among different cold-rolled steel products in the market. Manufacturers, contractors, and consumers can refer to the respective standards to select and use cold-rolled steel products that meet their requirements and applications.

Classification of cold-rolled steel
- Mild Steel: Mild steel is a type of cold-rolled steel known for its high flexibility, ease of machining, and cost-effectiveness. It is commonly used in the construction industry, manufacturing of household appliances, and various other applications.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel, a corrosion-resistant cold-rolled steel, finds extensive use in the food industry, healthcare, construction, and many other industrial sectors due to its high resistance to corrosion.
- Alloy Steel: Alloy steel, a type of cold-rolled steel, is created by blending steel with other alloying elements such as nickel, chromium, manganese, and molybdenum. This type of steel exhibits special mechanical and structural properties and is used in applications that demand toughness and durability.
Applications of cold-rolled steel in daily life
- Automotive and Transportation Industry: Cold-rolled steel is widely used in the production of automobiles and various modes of transportation, including cars, motorcycles, and trains. Its flexibility and durability meet stringent requirements in this industry.
- Construction and Mechanical Industry: In the construction and mechanical sectors, cold-rolled steel is employed for structural purposes, building frames, water pipes, and various other applications. Its ease of machining and strength make it an ideal material for construction projects and machinery.
- Electronics and Refrigeration Industry: Cold-rolled steel also plays a role in the electronics and refrigeration industry. It can be shaped into components such as pipes, screws, and other electronic accessories.
Advantages and disadvantages of cold-rolled steel
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1. High strength and relatively good corrosion resistance. | 1. Susceptible to corrosion in humid or chemically aggressive environments. |
| 2. Flexibility and ease of machining. | 2. Lower hardness compared to some other materials. |
| 3. Cost-effective compared to many other materials. | 3. Limited load-bearing and heat resistance compared to certain steel types. |
| 4. Available in various types and sizes. |
Distinguishing between hot-rolled steel and cold-rolled steel
Hot-rolled steel and cold-rolled steel are two different manufacturing processes and types of steel, each with its own characteristics and applications. Below is the distinction between these two types of steel:
| Criteria | Hot-rolled steel | Cold-rolled steel |
| Production process | The hot rolled steel production process is carried out at high temperatures. The steel raw material is melted and then passed through rolling mills to create the final steel sheet. This process heats the steel and changes its structure, resulting in a final product with high hardness and flexibility. | The cold rolled steel production process is carried out at room temperature or lower. After melting and forming the initial steel sheet, it is rolled through rollers under non-high-temperature conditions. This process helps maintain the original structure of the steel and creates a product with relatively low hardness. |
| Characteristics and applications | Hot rolled steel has good mechanical properties, resistance to deformation, and high strength. Therefore, it is often used in applications that require flexibility and load-bearing capacity, such as in construction, automotive, mechanical, and heavy industries. |
Cold rolled steel has lower hardness and higher flexibility compared to hot rolled steel. This makes it suitable for applications that require precision manufacturing, metal fabrication, the production of thin parts, and usage in the electronics industry and heat-sensitive industries. |
Conclusion
Cold rolled steel is an important material in the industrial sector with various applications. Through the production and heat treatment process, cold rolled steel can meet requirements for mechanical properties, load-bearing capacity, and corrosion resistance in many different fields. The development trend of the cold rolled steel industry focuses on advanced manufacturing technology and fabrication, as well as exploring new applications and potential developments in the areas of industrial and sustainable energy.
LEARN MORE
View more other products
Contact form